 |
| ||||||
In general about...
Discharging
More about Batscan...
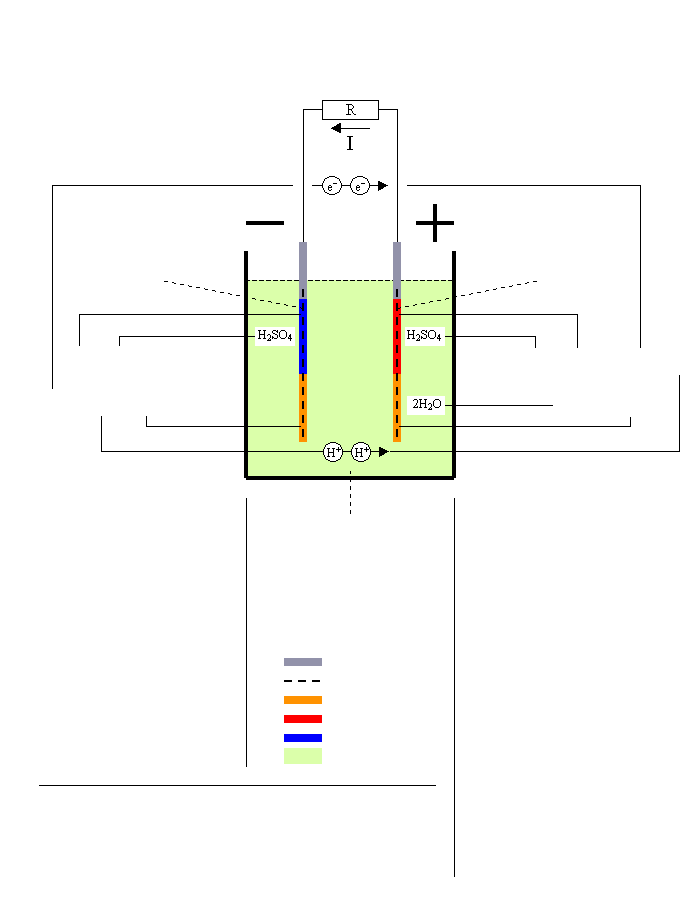
Discharging Lead/Acid Battery
Resistance
Negative plate = Anode
Pb → PbSO4
Sponge Lead → Lead Sulfate
E0 = -0.356V
Pb → PbSO4
Sponge Lead → Lead Sulfate
E0 = -0.356V
Pb + H2SO4
↓
[2e-] + 2H+ + PbSO4
↓
[2e-] + 2H+ + PbSO4
Reaction at -terminal
(Oxidation)
(Oxidation)
| 1. |
By removing two electrons [2e-] the lead oxidizes gets a positive charge: Pb → [2e-] + Pb2+ |
| 2. |
The positively charged lead atom reacts with the sulfuric acid and makes lead sulfate and two hydrogen
ions are released to the electrolyte: Pb2+ + H2SO4 → PbSO4 + 2H+ |
Electrolyte = Sulfuric Acid
H2SO4 → H2O
Sulfuric Acid → Water
H2SO4 → H2O
Sulfuric Acid → Water
Lead Electrodes
Grid Plate
Lead Sulfate
Lead Dioxide
Sponge Lead
Electrolyte
Grid Plate
Lead Sulfate
Lead Dioxide
Sponge Lead
Electrolyte
Net reaction at discharging
Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
Sponge Lead+Lead Dioxide+2 Sulfuric Acid→2 Lead Sulfate+2 Water
(chemical energy → electrical energy)
E = 2.041V
Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
Sponge Lead+Lead Dioxide+2 Sulfuric Acid→2 Lead Sulfate+2 Water
(chemical energy → electrical energy)
E = 2.041V
Positive plate = Cathode
PbO2 → PbSO4
Lead Dioxide → Lead Sulfate
E0 = +1.685V
PbO2 → PbSO4
Lead Dioxide → Lead Sulfate
E0 = +1.685V
H2SO4 + PbO2 + [2e-] + 2H+
↓
2H2O + PbSO4
↓
2H2O + PbSO4
Reaction at +terminal
(Reduction)
(Reduction)
| 3. |
The two added electrons [2e-] reduces the lead dioxide that splits into one lead ion(II)
and two oxygen ions: [2e-] + PbO2 → Pb2+ + 2O2- |
| 4. |
The lead ion from [3] reacts with the sulfuric acid and makes lead sulfate, and another two hydrogen ions are being released: Pb2+ + H2SO4 → PbSO4 + 2H+ |
| 5. |
The hydrogen ions from [2] and [4] joins with the oxygen ions from [3] and makes two water molecules: 2H+ + 2H+ + 2O2- → 2H2O |